Site investigations professionals follow a systematic approach consisting of five key steps. First, they define the investigation’s scope, establishing objectives and engaging stakeholders. Next, they conduct preliminary research, reviewing existing studies and identifying hazards. They then develop a detailed site investigation plan, focusing on strategic sampling locations. Fieldwork and data collection are conducted with precision to guarantee sample integrity. Finally, they analyze the data and report findings, assuring compliance and clarity. Further insights on these processes are available for exploration.
Key Takeaways
- Define the investigation’s scope, objectives, and engage stakeholders to ensure transparency and trust throughout the process.
- Conduct thorough preliminary research to identify existing data, hazards, and regional geological context.
- Develop a detailed site investigation plan, outlining assessment objectives, methodologies, and risk management strategies.
- Execute fieldwork with appropriate techniques, ensuring representative sampling and meticulous documentation of procedures.
- Analyze collected data rigorously, ensuring compliance with legal standards, and present findings clearly for stakeholder comprehension.
Define the Scope of the Investigation

Defining the scope of the investigation is a critical step in site investigations, as it establishes the boundaries and objectives of the study. This phase involves identifying key stakeholders and engaging them to guarantee their concerns and insights are integrated into the investigation process. Effective stakeholder engagement fosters trust and transparency, which are essential for regulatory compliance. The scope must delineate specific goals, methodologies, and anticipated outcomes, aligning them with applicable regulations and standards. Clarity in these parameters not only guides the investigation but also mitigates risks associated with non-compliance. By thoroughly addressing these elements, site investigation professionals can create a focused framework that supports informed decision-making and enhances overall project success. Additionally, proactive investigations can strengthen risk management and ensure that potential issues are identified and addressed early on.
Conduct Preliminary Research
Conducting preliminary research is essential for site investigation professionals, as it lays the groundwork for informed and effective decision-making. This phase typically involves a thorough literature review, enabling professionals to gather existing data and insights related to the site in question. By examining previous studies, reports, and geological surveys, investigators can identify potential hazards and site-specific challenges. Additionally, understanding the regional geology is vital; it provides context regarding soil composition, groundwater levels, and tectonic activity, all of which influence the investigation’s scope and methodologies. This foundational knowledge not only enhances the accuracy of subsequent assessments but also fosters a proactive approach to addressing environmental and structural concerns that may arise during the investigation process. Furthermore, utilizing professional investigative services can significantly improve the quality and reliability of site evaluations.
Develop a Detailed Site Investigation Plan
After completing preliminary research, the next step for site investigation professionals involves the formulation of a detailed site investigation plan. This plan must encompass a thorough site assessment, outlining objectives, methodologies, and anticipated outcomes. Professionals should identify specific locations for soil sampling, ensuring that sampling points are strategically chosen to represent the site’s variability. Additionally, the plan should address the types of analyses required for the collected samples, including physical, chemical, and biological assessments. A well-structured timeline and resource allocation are essential, as they facilitate efficient execution. Moreover, risk management strategies must be integrated, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and safety protocols. To enhance the integrity of the investigation, professionals may also consider employing digital forensics techniques, which can uncover crucial evidence related to site conditions. Ultimately, a robust investigation plan serves as a foundational document guiding subsequent fieldwork and data collection efforts.
Execute Fieldwork and Data Collection
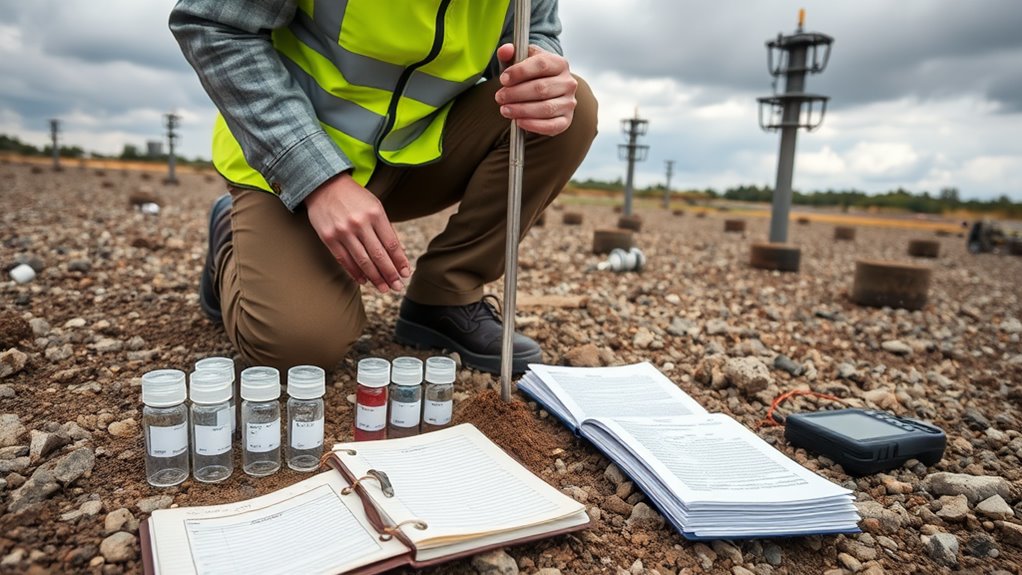

Executing fieldwork and data collection requires meticulous planning and adherence to the established site investigation plan. Professionals must select appropriate field techniques that align with the project’s objectives and the site’s specific conditions. This includes employing various sampling methods, such as grab sampling or composite sampling, to guarantee representative data is obtained. Each technique must be carefully executed to minimize contamination and maintain the integrity of the samples. Moreover, it is essential to document all procedures and observations meticulously, as this data will form the foundation for subsequent analysis. By rigorously following the protocols and employing systematic approaches, site investigation professionals can guarantee the reliability and accuracy of the collected data, ultimately supporting informed decision-making for future project phases. Additionally, hiring a professional investigator can provide access to specialized tools and techniques that enhance data collection efforts.
Analyze Data and Report Findings
Analyzing data and reporting findings are critical stages in the site investigation process, as they translate raw field data into actionable insights. This phase involves meticulous data interpretation, where professionals assess and synthesize collected information to identify patterns, anomalies, and correlations. Utilizing advanced analytical tools and techniques, they guarantee accuracy and reliability in their findings. Additionally, ensuring compliance with legal principles is vital to maintain the integrity of the investigation process.
Once analysis is complete, the findings presentation becomes paramount. Clear and concise reporting is essential, as it communicates complex information to stakeholders in an understandable manner. Visual aids, such as graphs and charts, enhance comprehension and engagement. Ultimately, this process not only informs decision-making but also fosters trust between professionals and clients, establishing a foundation for future collaboration and project success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Qualifications Are Required to Become a Site Investigation Professional?
To become a site investigation professional, individuals typically require relevant educational qualifications, such as a degree in geology or engineering. Additionally, completion of certification programs enhances expertise, ensuring adherence to industry standards and best practices.
How Do I Choose the Right Tools for Site Investigations?
Choosing the right tools for site investigations involves careful site selection and thorough equipment comparison. Analyzing project requirements, environmental conditions, and specific geological characteristics guarantees ideal tool selection, enhancing data accuracy and overall investigation effectiveness.
What Safety Measures Should Be Taken During Fieldwork?
During fieldwork, implementing safety measures involves conducting a thorough risk assessment and utilizing appropriate personal protective equipment. These practices guarantee the safety of personnel while minimizing hazards associated with various environmental and operational conditions encountered on-site.
How Can I Improve My Data Analysis Skills?
To enhance data analysis skills, one should engage in regular practice using statistical software, focusing on data visualization techniques. Immersing in real-world datasets fosters deeper understanding and proficiency in interpreting complex information effectively and meaningfully.
What Are Common Challenges Faced During Site Investigations?
Common challenges during site investigations include budget constraints limiting resource allocation and site access issues that hinder thorough assessments. These factors can greatly impact the accuracy and effectiveness of the investigation outcomes, complicating project timelines and objectives.
Conclusion
To summarize, the outlined five steps for site investigations professionals provide a structured approach to ensuring thorough evaluations. By defining the investigation’s scope, conducting preliminary research, and developing a detailed plan, professionals can effectively guide the execution of fieldwork and data collection. The subsequent analysis of collected data, followed by precise reporting of findings, reinforces the integrity and reliability of the investigation process, ultimately facilitating informed decision-making in environmental and engineering contexts.